Shanghai Gengyun Industrial Co., Ltd
What is the difference between Single mode and Multimode Fiber Optic Cable? How to Choose?
Single-mode fiber (usually yellow) is suitable for long-distance communication transmission, and multimode fiber (usually orange, aqua blue and other colors) is suitable for short-distance communication transmission. This article will introduce the difference between single mode and multimode fiber optic cable in detail.
What is Single Mode Fiber Optic Cable?
In fiber optic communication, single-mode fiber (SMF) is a fiber that directly transmits light signals in the transverse mode. Single-mode fiber operates at a data rate of 100M/s or 1G/s, and the transmission distance can reach at least 5 kilometers. Usually, single-mode fiber is used for long-distance signal transmission.
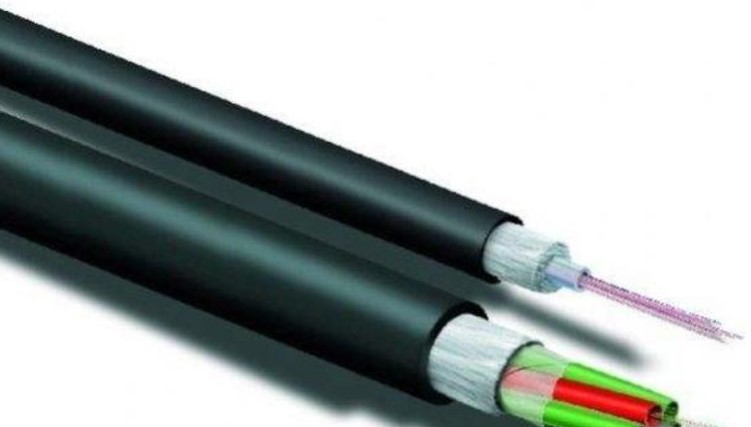

What is Multimode Fiber Optic?
Multimode fiber (MMF) is mainly used for short-distance fiber optic communication. Such as within a building or on a campus. The typical transmission speed is 100M/s, and the transmission distance can reach 2km (100BASE-FX). 1G/s can reach 1000m, and 10G/s can reach 550m. There are two types of refractive index: graded refractive index and step refractive index.
Basic differences between single-mode and multi-mode optical fibers
Single-mode optical fibers (Single Mode Fiber) transmit in one mode. The fiber core is 9μm, and the rate is 100M/s or 1G/s. The transmission distance is more than 5km, and the light source is a laser light source. The cable color is mostly yellow, and the connector is mostly blue or green. The applicable wavelength is 1310nm~1550nm.
Multi-mode optical fibers (Multi Mode Fiber) support multiple modes of transmission. The fiber core is 50μm/62.5μm, and the typical rate is 100M/s. The transmission distance can reach 2km. 1 G/s can reach 1000m, 10 G/s can reach 550m, and the light source is an LED light source. The cable color is orange for Gigabit and water blue for 10 Gigabit. The connector is mostly grayish white, and the applicable wavelength is 850nm/1310nm.
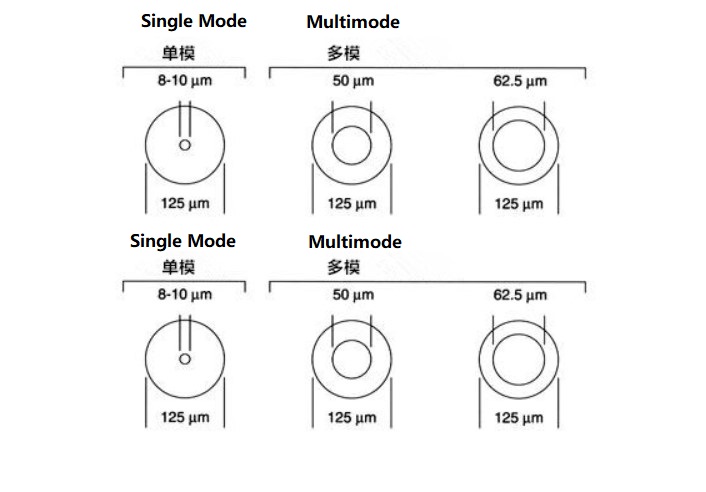
Classification of Single Mode and Multimode Optical Fibers
Single-mode optical fibers include G652, G655, and G657. Multimode optical fibers include OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5.
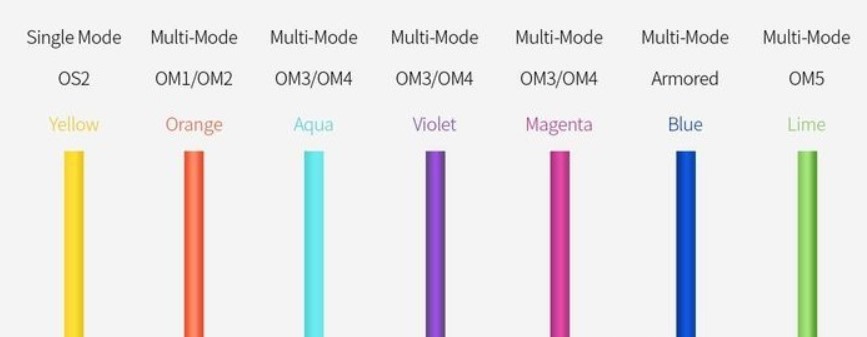
Most new OM5 fiber optic patch cords are lime green. Compared with OM4 fiber optic patch cords, OM4 only supports single wavelength transmission at a time. OM5 can support 4 wavelengths at a time, and the transmission distance is longer, which will be widely used in 40G/100G data center cabling. OM1/OM2 is widely used indoors, mostly orange. OM3/OM4 is mostly aqua blue, but also violet, magenta, etc. It is mostly used in data centers for 10G-40G/100G.
Since Single Mode Fiber Optic Can Transmit Longer Distances, Why not Use Single Mode Fiber?
The biggest difference from single mode fiber is that multimode fiber has a larger diameter. The larger core diameter means that multimode fiber can support multiple transmission modes. Although this makes it more expensive than single mode fiber. However, single mode fiber mostly uses solid-state laser diodes as light sources. Multimode fiber mostly uses LEDs as light sources, and it is obvious that the former’s equipment is more expensive than the latter’s. As a result, the cost of using multimode fiber is much less than that of using single mode fiber. In addition, under short-distance optical transmission conditions, especially in LAN cabling scenarios, multimode fiber works just as well as single-mode fiber. Therefore, driven by cost advantages, multimode fiber is more suitable for data center construction.
Single mode vs Multimode Fiber Optic, the Specific Differences
1.Core Diameter
The main difference between single mode and multimode fiber optic cable is that the former has a larger diameter, usually 50 or 62.5m core diameter, while typical single-mode fiber is 8 and 10m core diameter, and both have a cladding diameter of 125m.
2.Light Source
Usually both lasers and LEDs are used as light sources. Laser light sources are significantly more expensive than LED light sources because the light they produce can be precisely controlled and has high power. While LED light sources produce more dispersed light (many modes of light), these light sources are mostly used in multimode fiber patch cords. At the same time, laser light sources (producing light close to a single mode) are usually used in single-mode fiber patch cords.
3.Bandwidth
Since multimode fiber has a larger core size than single-mode fiber, it supports multiple transmission modes. In addition, like multimode fiber, single-mode fiber also exhibits modal dispersion caused by multiple spatial modes, but the modal dispersion of single-mode fiber is smaller than that of multimode fiber. For these reasons, single-mode fiber has a higher bandwidth than multimode fiber.
4.Sheath Diameter
The color of the sheath is sometimes used to distinguish multimode fiber patch cords from multimode fiber patch cords. According to the TIA-598C standard definition, for non-military use, single-mode fiber uses a yellow outer sheath, and multimode fiber uses an orange or aqua outer sheath. Depending on the type, some manufacturers use purple to distinguish high-performance OM4 fiber from other types of fiber.
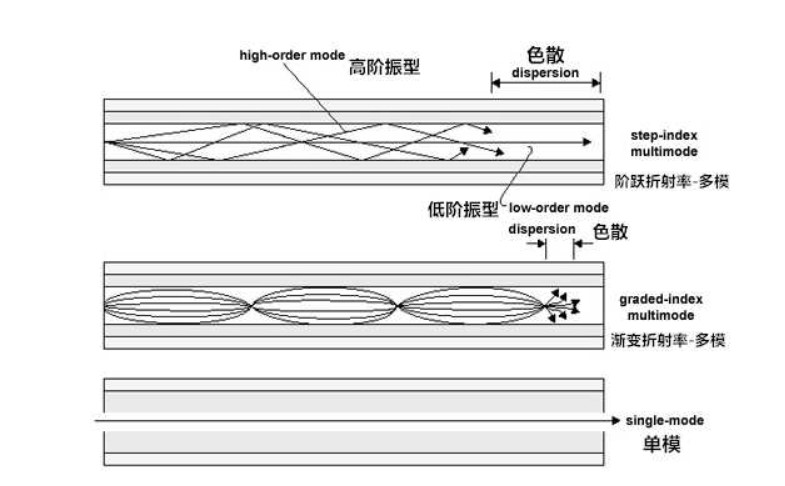
5.Modal Dispersion
LED light sources are sometimes used in multimode fiber to create a series of wavelengths that propagate at different speeds. This will cause multimodal dispersion, which limits the effective transmission distance of multimode fiber patch cords. In contrast, the laser used to drive single-mode fiber produces a single wavelength of light. Therefore, its modal dispersion is much smaller than that of multimode fiber. Due to modal dispersion, multimode fiber has a higher pulse expansion rate than single-mode fiber, which limits the information transmission capacity of multimode fiber.
6.Price
For multimode fiber, which can support multiple light modes, its price is higher than that of single-mode fiber. But in terms of equipment, since single-mode fiber usually uses solid-state laser diodes, single-mode fiber equipment is more expensive than multimode fiber equipment. Therefore, the cost of using multimode fiber is much less than the cost of using single-mode fiber.
Single Mode vs Multimode Fiber Optic, How to Choose?
Considerations of the transmission distance to be covered and the overall budget. If the distance is less than a few miles, multimode fiber will work well. The cost of the transmission system (transmitter and receiver) will range from $470 to $757. If the distance to be covered exceeds 6-10 kilometers. Single-mode fiber should be selected. But due to the increased cost of laser diodes. The cost of the transmission system will usually exceed $957.
A mode is a possible energy distribution state of light in the fiber. At the same wavelength, the thicker the fiber, the more modes it can accommodate. At the same fiber diameter and refractive index, the shorter the wavelength of light, the more modes the fiber can accommodate. So usually multimode fiber is thicker than single-mode fiber of the same wavelength.
For single-mode fiber, all the propagated energy is in one mode. Usually the lowest HE11 mode. For multimode fiber, the propagated energy is shared among the various modes. And the energy can be redistributed among different modes as the fiber is bent. So the energy distribution of the emitted light is easily changed after the multimode fiber is touched, bent and deformed. In contrast, when a single-mode fiber is touched, the emitted light is basically unaffected. The mode is the distribution structure of the electromagnetic wave. Multimode fiber has multiple modes, while single-mode fiber can only propagate in one mode.
(1) From the Perspective of Structure
The core of a single-mode fiber is small (8-9 microns). The core of a multimode fiber is relatively large (50-62.5 microns). The outer diameter of the fiber is generally 125 microns.
(2) From the Perspective of Refractive Index
The core of a single-mode fiber is a uniform high refractive index. It matches the refractive index of the cladding according to a certain reporting aperture (NA). It forms a single-mode form at the application wavelength (only supports the fundamental mode).
There are two types of multimode fiber cores: the step-index type has a uniform core. The graded-index type has a structure with a high center and a gradually decreasing refractive index around it. Depending on the bandwidth, there are OM1, OM2…OM5. It can form “self-focusing”.
(3) From the Perspective of Application
Single-mode fiber is generally used for long-distance transmission. Multimode fiber is mostly used in data centers.
Energy fiber (laser application) may also use multimode. However, for non-communication applications, the optical performance of interest is completely different.
