Shanghai Gengyun Industrial Co., Ltd
What is Cat 6 UTP Cable? The Complete Guide for Network Builders

The Essential Link in Modern Networks
Cat 6 UTP cable forms a fundamental part of today’s structured cabling systems. It provides a mature, reliable, and cost-effective way to transmit data at high speeds. This cable serves as the primary physical medium for Gigabit networks and can even support shorter 10-Gigabit connections. You find it everywhere: in office buildings, schools, data center access layers, and smart homes. It acts as the silent, critical network backbone that powers our connected world.
- The Journey to Category 6
Network cables have evolved to meet growing demands for speed and clarity. Each step from Cat 3 to Cat 5e improved bandwidth and reduced signal interference. The industry standardized Category 6 in the early 2000s, marking a major leap. It doubled the usable frequency to 250 MHz and introduced tighter controls for crosstalk. This advancement addressed the need for 1 Gbps networks and prepared for future 10 Gbps use. For nearly two decades, Cat 6 has remained the smart, forward-looking choice for new installations.
- The Advantage of the UTP Design
The “UTP” in its name stands for Unshielded Twisted Pair. This design remains key to its popularity. Unlike shielded cables, UTP relies on a clever, balanced approach for performance. It uses precisely twisted copper pairs and often a central separator to keep them apart. This geometry, combined with differential signaling, allows the cable to naturally cancel out electromagnetic interference (EMI) it encounters. The absence of a shield makes the cable more flexible, much easier to connect, and removes the need for complex grounding required by shielded systems.
Technical Design and Key Specifications
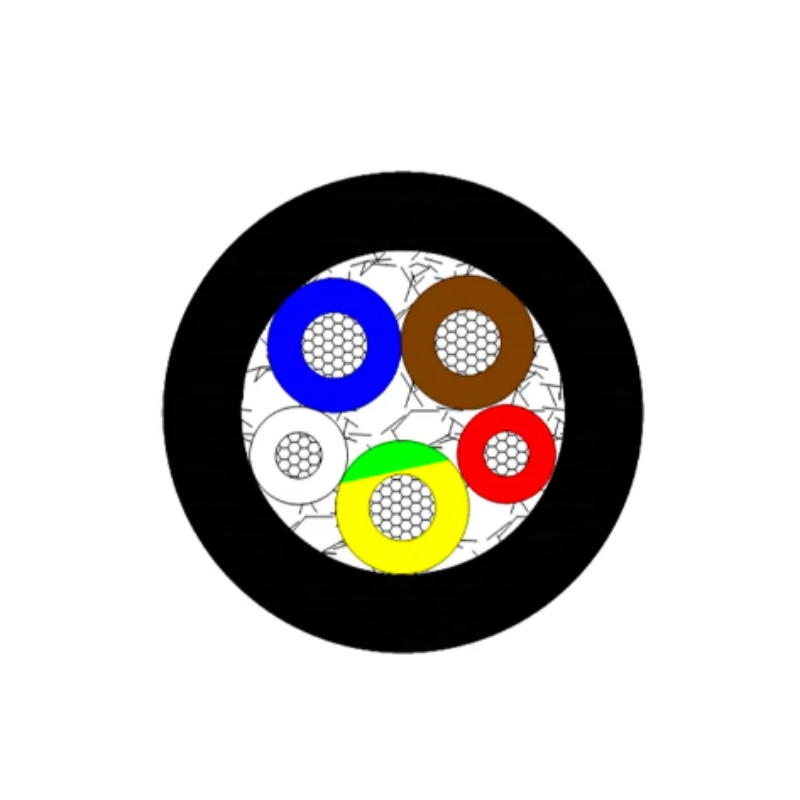
Consistent performance stems from strict international standards and precise manufacturing. The design optimizes electrical behavior within a simple, robust structure.
- Internal Construction: Conductors and Isolation
The core contains four twisted pairs of oxygen-free copper (OFC) wires, usually 23 AWG thick. Manufacturers give each pair a unique, precise twist rate. Varying these rates is a primary method to minimize crosstalk—unwanted signal leakage between pairs. Many high-quality Cat 6 cables include a longitudinal spline or separator. This plastic spine runs the cable’s length, keeping the four pairs physically apart. This isolation greatly improves critical performance metrics like Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT), which is essential for high-speed data transmission using all four pairs.
- Electrical Performance and Supported Standards
A fully compliant Cat 6 UTP link (up to 100 meters including patch cords) certifies for key applications
- Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T): Fully supported over the entire 100-meter distance.
- 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GBASE-T): Officially supported for runs up to 55 meters at the full 250 MHz bandwidth.Its performance depends on parameters like characteristic impedance, insertion loss (signal weakening), and return loss. A positive Attenuation-to-Crosstalk Ratio (ACR), which is a signal-to-noise measure, is required for a clear channel.
- Outer Jacket and Safety Compliance
An outer sheath protects the insulated pairs. Common sheath materials are:
- PVC: The most common, cost-effective option with good durability and flame-retardant ratings (CM, CMR, CMP).
- LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen): Used in air-handling spaces and areas with many people. It produces minimal smoke and no toxic gases if burned.
- PE (Polyethylene): Used for outdoor or direct burial versions due to superior moisture resistance.The jacket choice ensures the cable meets local building fire safety codes and environmental needs.
Application in Structured Cabling Systems
Cat 6 UTP is the definitive standard for horizontal cabling—the permanent run from a wiring closet to a workstation outlet.
- Its Role in the Network Ecosystem
In a standard setup:
- Installers run the cable in walls and ceilings from a patch panel to a wall plate.
- They terminate it onto an RJ45 keystone jack at the plate.
- A short patch cord connects a device (computer, phone, access point) to the jack.
- In the closet, another patch cord links the patch panel to a network switch.This creates a complete, standardized channel for reliable connectivity. It works seamlessly with older equipment while ready for current and future high-speed demands.
- Comparison with Other Cabling Options
- vs. Fiber Optic Cable: Cat 6 UTP rules the “last 100 meters.” It is less expensive, easier to terminate, and delivers Power over Ethernet (PoE). Fiber is better for very long distances, extreme bandwidth, or total immunity to interference.
- vs. Cat 6A/ Cat 7: Cat 6A supports 10GBASE-T over 100m and has better alien crosstalk control but is thicker and costlier. Cat 6 remains the optimal balance of price and performance for most Gigabit networks where 10G is not immediately needed at every location.

Future Relevance and Conclusion
- Even with advances in Wi-Fi and fiber, a robust wired Cat 6 UTP infrastructure remains vital for stable, secure, and power-delivering connections.
- This cable is well-suited to support emerging needs like advanced PoE (PoE++) for high-power devices and the proliferation of IoT and building automation systems. To ensure it performs as rated, installers must follow best practices: maintain the proper bend radius, avoid overtightening cable bundles, use correct termination techniques, and—most importantly—test and certify every installed link with professional equipment.
- In conclusion, Cat 6 UTP cable is the proven and indispensable workhorse of modern network infrastructure. Its clever unshielded design balances high performance (supporting up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet over shorter runs) with ease of installation and cost-effectiveness. As the backbone of structured cabling systems, it reliably connects devices across enterprises, schools, and homes. With its inherent capability to deliver both data and power via PoE, Cat 6 UTP is not just a legacy standard but a continuing relevant solution, ready to support next-generation IoT and connected building technologies for years to come.
FAQs
1. What’s the real difference between Cat 5e and Cat 6 cable?
The main differences are in bandwidth and crosstalk control. Cat 5e is rated for 100 MHz and supports 1 Gigabit Ethernet. Cat 6 is rated for 250 MHz, has stricter crosstalk limits, and includes alien crosstalk specifications. This allows Cat 6 to support 10 Gigabit Ethernet up to 55 meters and provides greater signal integrity and future-proofing for Gigabit networks.
2. Do I need special connectors for Cat 6 UTP cable?
For optimal, certified performance, yes. While you can use Cat 5e-rated plugs and jacks, to guarantee a true Cat 6 channel, all components (cable, jacks, patch panels, cords) should be Cat 6 rated or higher. Cat 6 connectors have more precise internal designs to maintain the cable’s high-frequency performance at the connection points.
3. Can I run standard Cat 6 UTP cable outdoors?
No. Standard indoor-rated cable should never be installed outside. Its jacket will degrade from sunlight and moisture. For outdoor runs, you must use a specifically designed Outdoor Rated Cat 6 Cable. This type has a UV-resistant jacket, may be gel-filled, and often includes additional protection features.
4. What’s the difference between solid and stranded Cat 6 cable?
They are designed for different jobs.
• Solid Conductor: Used for permanent in-wall installations. The single, solid wire offers better electrical performance over distance and is more durable when terminated into jacks and panels.
• Stranded Conductor: Used for patch cords. The many fine strands make it very flexible for frequent movement. It has slightly higher signal loss, but this is not an issue for short cord lengths.
Company Introduction: With over 20 years of deep industry expertise, we specialize in customizing and supplying solutions for optical fibers, cables, raw materials, and manufacturing equipment. We deliver reliable technical support and product services.
About the Author: With 20 years of hands-on experience in optical transmission media, cable assemblies, and core substrate materials, we offer practical, expert insights grounded in full-industry-chain expertise.
